Impact case to drive the focus on value
In the HDM the impact case helps the project owner, the project leader and selected key stakeholders to understand and align on the intended value creation of the project. Furthermore, the impact case adds the perspective of who needs to change behavior to realize the intended business impact. This method combines quite a few of the PMBOK Guide principles into one: Effectively engage with stakeholder, Focus on value, Tailor based on context and Enable change to achieve the envisioned future state. The impact case method and tool (called artifact in PMBOK Guide) can be a value adding and to-the-point element to add to the performance domains of “Planning” and “Measurement” to drive focus on value in the project.
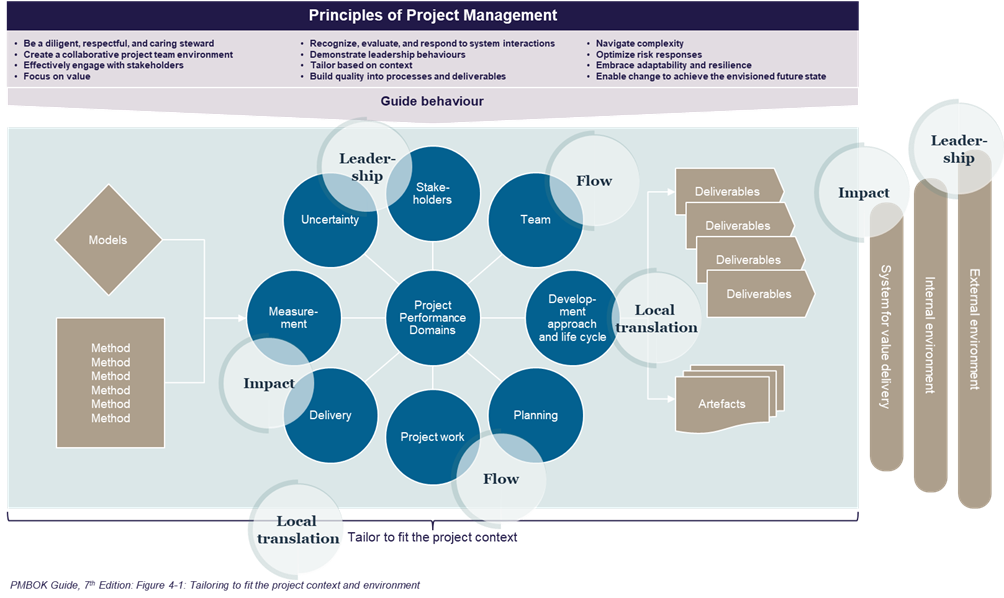
To put is short the PMBOK Guide still have a strong focused on producing the project deliverables in performance domains such as Delivery, Planning and Project Work. The HDM has strong focus on creating the impact, breaking down the impact and understanding the impact journey throughout the project life. This is evident in the strong and direct link between impact principle and impact methods (e.g. Impact solution design) in HDM which can inspire the PMBOK Guide practitioner in where to focus their efforts and use the encouraged tailoring.
High allocation can increase intensity and project flow
The performance domain of Team, Project work, and Development approach inspires on how to execute the project. There is a lot of inspiration to pick from in the PMBOK Guide favouring a tailored fit to many kinds of projects. The HDM can help the PMBOK Guide practitioner in two obvious ways; First of all the flow principle of creating “High intensity and frequent interaction to ensure continuous project progression” is translated into a rule of thumb allocating the core team min. 50% to the project. By adding this perspective, the project effectiveness in the three performance domains above can be enhanced. Secondly a strong Rhythm in key events can help to benefit stakeholder interaction on a frequent basis which is strongly emphasised – but not handled – in the stakeholder performance domain in the PMBOK Guide. Again, the strong link between principle and methods in the HDM can help the PMBOK Guide practitioner in where to put their efforts.
Leadership - the sponsor plays a vital role
In the HDM Leadership is key to increase project success. In the PMBOK Guide Leadership also is highlighted as an important principle (Demonstrate leadership behaviours). However, the Sponsor is not addressed in the methodology as such but instead the role is described in the Appendix X2 as an add-on. In the HDM the importance of the sponsor is underlined as one of nine methods (The active project owner). In the PMBOK Guide the project manager is perceived as being the sole responsible person for the project. In the HDM the project owner / sponsor and the project manager are all together in this endeavour with a shared accountability and responsibility. Highlighting this critical role and the dynamic leadership relationship between the sponsor and the project manager as the most important roles in a project could benefit the PMBOK Guide approach.
Using the 3 leadership methods in HDM can guide sponsor and project manager to be reflective and adaptive in their mindset – helping them to set a live the PMBOK Guide principles of Systems Thinking, Tailoring, Complexity, and Adaption and resilience.
Summarising
The new principle based PMBOK Guide 7th edition and the HDM are complementary and overlapping in its thinking and approach to project management. The previous process-based and prescriptive approach of the PMBOK Guide 6th edition has been left behind. Now, they both focus on effective project management and intended outcomes rather than adherence to processes.
The HDM can certainly benefit from the comprehensive and exhaustive approach of the PMBOK Guide. Especially the extensive online toolbox for models, methods, and artefacts is a source of inspiration for local translation of Half Double projects. However, the opposite is as also the case as the PMBOK Guide can benefit from the simplification, the focus and the strong link between principles, methods and tools embedded in the HDM. Especially the leadership dynamic and shared responsibility between the sponsor and the project manager can increase the effectiveness of the project and the project outcome.
In the cross-reference overview/table below, you can investigate for more PMBOK Guide elements supporting the HDM.
Download the full document "Coexistence between Half Double and PMI" underneath.