How Half Double can coexist and interact with SCRUM

Introduction
Purpose
The general purpose of the co-existence descriptions is to provide information to the project society as to how the Half Double Methodology (HDM) can be used in combination with existing Project Management and Agile standards, models, methodologies, and frameworks currently being used by many project-oriented organizations.
Target group
This specific co-existence description is targeted to the group of people and organizations currently applying the Scrum framework and who are now considering or determined to also adopt, implement and apply the Half Double Methodology (HDM). This document will inform how Scrum can benefit from being used in combination with HDM and vice versa.
Technical knowledge of projects and project management, agile initiatives, and agile project management, the HDM 1.0 and The Scrum Guide 2020, version 5.0, is a prerequisite for being able to understand this document. Scrum references are mainly based on Ken Schwaber & Jeff Sutherland, currently associated with Scrum.org.
A project management methodology and a framework
In this document, we are looking at project management methodology (HDM) and a project management framework (Scrum). A Methodology is defined as an organized collection of principles, methods, techniques, practices, procedures, and rules used by those that work in a discipline. To put it simple a project methodology will pick and choose between different methods and practices to fulfill its purpose in a given project. It is based on a few principles set alive in the project.
A framework on the other hand is an essential supporting structure which other things are built on top of. To put it simple a framework is a basic conceptional structure (as of ideas) for the practitioner to follow. Hence a framework is more focused on following the conceptual structure (Scrum) as opposed to following the principles indicated (HDM).
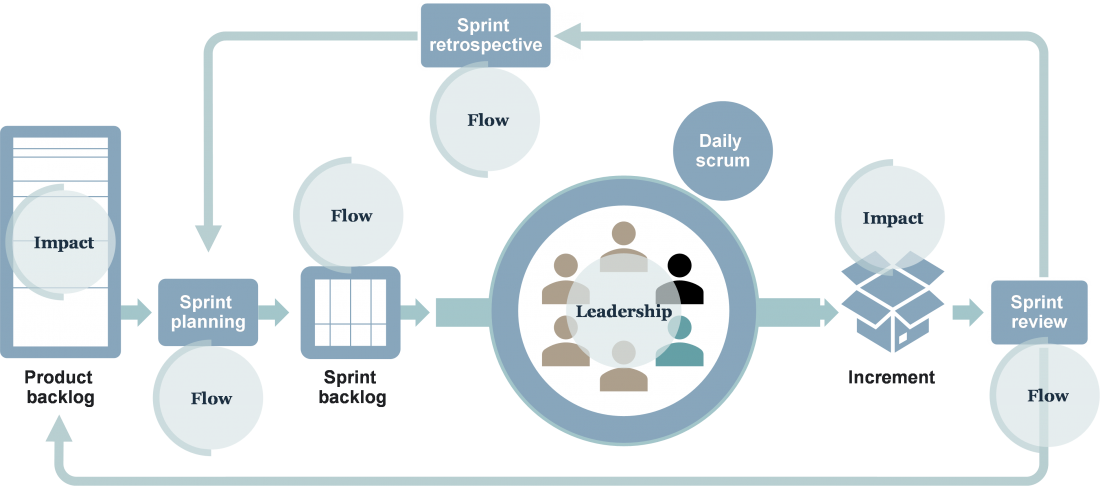
Grafical illustration of the interactive “hot spots” between Scrum (5.0) and HDM (1.0)
The illustration provides an overview of how the HD methodology and the Scrum framework overlap and interacts with each other. The conclusion is evident: The two concepts a very similar in nature and relate closely to each other in most aspects as they are both build on simplicity and the collective intelligence of the people using it. The flow elements in both concepts are very similar. However, the main difference is found in a broader project management and principle-based understanding, wide stakeholder inclusion and value creation breakdown with stakeholders (HDM) as opposed to a software development and structure-based understanding, enhanced self-managing team focus, and a narrow product definition created exclusively by the Product Owner (Scrum). The illustration is based on the information in the cross-reference guide list in Annex 3.
How the Scrum framework (5.0) will benefit from being used in combination with the Half Double Methodology (HDM 1.0) and vice versa
Introduction
Scrum and HDM are similar as they are both build on simplicity and the collective intelligence of the people using it. They are both created as open-source concepts and are available for free to download for the benefit of practitioners all over the world. They are inspired by Lean thinking (reduce waste) and empiricism (knowledge from expertise) and both employs an iterative, incremental approach. The concepts make visible the relative efficacy of current management, environment, and way of working, so that improvements can be made – e.g., the lack of 50% core team allocation in HDM will make it evident that the project is not progressing every week as it should. So, at the surface the two concepts are very similar and could be considered mutually exclusive.
However, they are not.
Scrum derives from software development and is based on a “continuous improvement mindset” of a platform consisting of multiple products. The Scrum framework is designed as a structure for an “execution engine” with own role definition that differ from traditional project management roles (e.g., Scrum Master). Furthermore, self-management of the Scrum team is highlighted as key and at the same time the Product Owner is made solely accountable and responsible for defining value creation. This help to reduce complexity and can certainly be helpful in a lot of projects.
The Scrum framework is an immutable simple structure, that is intended to be supplemented with techniques, methodologies, and practices in order to reach its goal. All Scrum implementations have therefore added practices that the organisation regards as integral in order to succeed with Scrum.
HDM derives from a broader project management tradition and principle-based approach. It acknowledges projects as a “complex and unique endeavor” where change leadership and broad stakeholder satisfaction are considered critical to succeed. This makes key stakeholders just as important as the team. Hence key stakeholders play an essential role in defining the impact and are directly involved in many project events.
The Half Double methodology will enrich the Scrum framework with certain methods and practices that specifically can strengthen the ability to reach the desired impact. The Scrum framework on the other hand provides a certain firmness to the events and artifacts needed to create a strong flow and can in this area supplement the Half Double methodology.
Employing Half Double and Scrum together will require a translation of terminology in certain areas and whereas Half Double explicitly is open for local translation, the Scrum framework is only open for extension.
The product goal and impact
“Stakeholder satisfaction” is the ultimate success criteria”, is the main message of the Impact principle of Half Double and perhaps the most important statement of Half Double. The overall goal of Half Double is to create more impact in less time, but also recognise that this is a complex process that benefits from being iterative and including many stakeholders. Therefore, the HDM process includes a value creation breakdown with stakeholders ultimately defining the deliverables in the end of the process. The project lead should be firm on the impact and flexible on the deliverables to succeed and create key stakeholder satisfaction.
In Scrum a narrow product definition created exclusively by the Product Owner defines the value creation. Scrum teams could as an example add the concept of Impact Solution Design, which is a process of high involvement across stakeholders, where the desired impact becomes clearer and ideas for creating early impact are generated collaboratively. This process and tool can greatly enhance the quality of the Product Goal and the Product Backlog in Scrum, especially when incorporating deliveries that are intended to create behavioural impact.
Whereas Scrum is centred around a Product, defined in the Scrum Framework as “A vehicle to deliver value.”, Half Double is centred around the value itself - defined as Impact. Half Double can thus facilitate more deliberate discussions on how the Product Goal should be defined and altered over time.
Furthermore, the pulse check in HDM can be a valuable input to the Scrum Sprint Review in order to gain insight to key stakeholders’ current attitude and satisfaction.
HDM could on the other hand be inspired by the Product Backlog and Sprint Backlog link to convert Impact Solution Design core ideas to tangible deliverables with Definitions of Done associated to them.
Sprints and flow
The Scrum Framework and Half Double have significant complementary overlap in the approach to create flow with sprints and visual planning. An organisation that decides to supplement a working Scrum implementation with Half Double will not experience any notably difference in the ability to create flow in the delivery of work items.
Subtle differences exist, i.e., the Scrum framework does not explicitly address the allocation (50% of time) or location of a “Developer” (a team role in Scrum) whereas the Half Double addresses the need for high allocation and co-location of any team member in order to generate weekly progression of the project.
The Scrum Sprint Retrospective can be an inspiration for the HDM pulse check feedback session. Also, the 4 Sprint events (sprint planning, daily scrum, sprint review, and sprint retrospective) can be more firmly defined and executed helping to optimize the project flow.
Scrum teams and leadership
Both Scrum and Half Double explicitly address the leadership dimensions with a clear distinction between the owner and the leader role. The Scrum guide and the Half Double handbook explains in different terminology how these two roles interact and collaborate to create the highest value in the shortest time. However, the shared key in both frameworks is that the people in the two roles must be reflective and adaptive
The Project Owner (HDM) and the Product Owner (Scrum) leads the impact creation, and each owns the impact (HDM) and the product (Scrum). They are both accountable for maximizing the value of the project / the product and the owner is one person, not a committee.
The Project Leader (HDM) and the Scrum Master (Scrum) are both considered people leaders and acknowledges that progress in created through people and their ingenuity, creativity and motivation. The project leadership in HDM is although seen as a broad stakeholder responsibility.
However, in HDM the relationship between the Project Owner and the collaborative Project Leader are underlined as the strongest relationship described as a “dynamic duo” in it together. In Scrum the relationship between the Scrum Master and the Developers are underlined as the strongest relationship illustrating the difference in approach – broad stakeholder leadership at management level (HDM) versus product creation at team level (Scrum). Each concept can benefit from inspiration and add on at the overall impact level and at the product creation level.
Summarising
Scrum and Half Double are good supplements, where the main difference is the language used around the impact creation and broad stakeholder involvement.
Scrum has a strong language around Products, which in common use has been supplemented with terminology such as User-stories, Epics, story-points, etc. The Scrum framework and common Scrum related practices can therefore add a certain rigour to Half Double when applied on product development.
Half Double has a project and impact focused terminology that builds on project management terminology and is incorporating behavioural change as a prerequisite for benefit realization. Supplementing Scrum with Half Double can therefor add value in an organisation, that is used to project terminology and requires that work be budgeted as projects, as well as expanding the scope for the team to include change management.
The main choice between the two concepts can depend on the project type. A main guideline is that Scrum has its sweet spot with software projects whereas Half Double has its sweet spot with strategy execution and internal transformation projects.
Download the full document "Coexistence between Half Double and Scrum" underneath.
Scrum and Half Double are good supplements, where the main difference is the language used around the impact creation.
For more descriptions of Half Double's coexistence with other PM standards clic…Grafical illustration of the interactive “hot spots” between Scrum (5.0) and HDM (1.0)